Cows’ Milk Protein Allergy
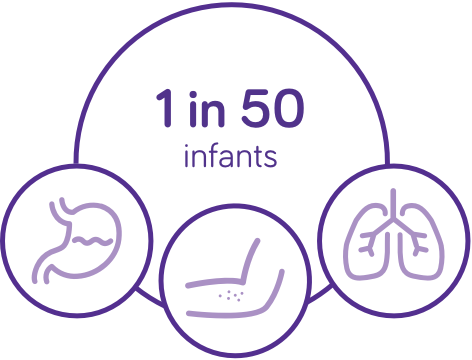
1 in 50 infants are allergic to cows’ milk protein & symptoms can persist until 3 to 5 years of age2
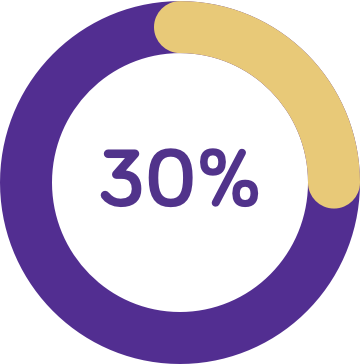
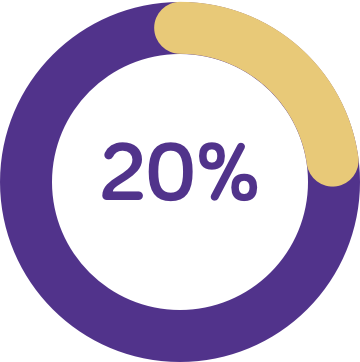
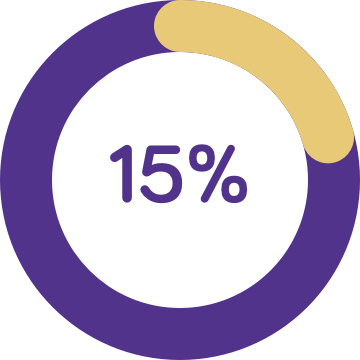
The majority (92%)5 of children with cows’ milk protein allergy experience 2 or more symptoms, which may be6:
- Skin related: including eczema, hives, swollen lips face or eyes
- Gastrointestinal: including reflux, vomiting, diarrhoea, colic, back arching, not feeding
- Respiratory: including wheezing or noisy breathing