
Immunity and gut dysbiosis
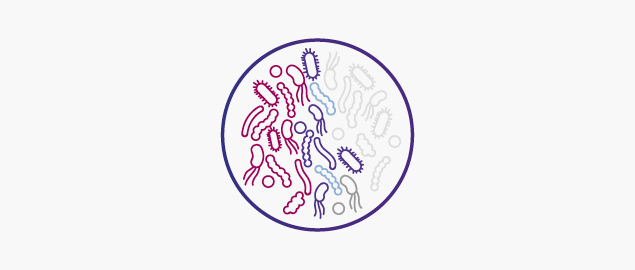
Gut dysbiosis and CMPA
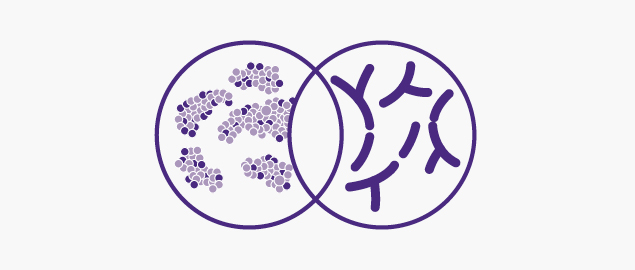
CMPA and synbiotics
Useful Resources
Synbiotic clinical paper summaries

Expert webinar: Gut and Immune Health
MD BriefCase: Product Brief

Expert webinar: Synbiotics in allergy management
Allergy Podcast Series

Clinical benefits of SYNEO™
SYNEO™ is the only CMPA range to contain a unique, patented blend of pre- and probiotics, inspired by components of breast milk, that work together to help promote a healthy gut microbiota and support immune system development.14–17
In clinical trials involving infants with CMPA, addition of SYNEO™ demonstrated:13–16,18,19
Discover how the SYNEO™ range could make a difference to your patients with CMPA

Neocate® SYNEO™

Aptamil® AllerPro SYNEO™ Infant Formula (0-6 months)

Aptamil® AllerPro SYNEO™ 2 (6-12 months)
Support for you and your patients
Join now and learn about our education events, research initiatives and evidence-based resources – furthering your professional development and clinical practice.
References:
1. Vighi G et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;153(Suppl 1):3–6.
2. Azad M et al. Clin Exp Allergy 2015;45:632–43.
3. Kirjavainen P et al. Gut 2002;51:51–5.
4. Mitsuoka T. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 2014;33:99–116.
5. Roger LC et al. Microbiology 2010;156:3329–41.
6. Abrahamsson TR et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129:434–40.
7. Harvey BM et al. Pediatr Res 2014;75:343–51.
8. Candy DCA et al. Pediatr Res 2018;83:677–86.
9. West CE et al. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 2015;135:3–1.
10. Kim BJ et al. Allergy Asthma lmmunol Res 2014;6:389–400.
11. Azad MD et al. BJOG 2016;123:983-93.
12. Sackesen C et al. Front Pediatr 2019;7:372.
13. Van der Aa LB et al. Clin Exp Allergy 2010;40:795–804.
14. Fox AT et al. Clin Transl Allergy 2019;9:5.
15. Jeurink PV et al. Benef Microbes 2013;4:17–30.
16. Scholtens PAMJ et al. J. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 2012;3:425–447.
17. Martin R et al. Benef Microbes 2010;1(4)367–82.
18. Burks A et al. Pediatr Allergy lmmunol 2015;26:316-22.
19. Chatchatee P et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2021; doi; 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.06.025 [Epub ahead of print].
